Navigating the complex world of healthcare can be overwhelming, especially when it comes to understanding the differences between Medicare and Medicaid. These two government-funded healthcare programs are often confused with one another, but they serve distinct purposes and cater to different segments of the population.
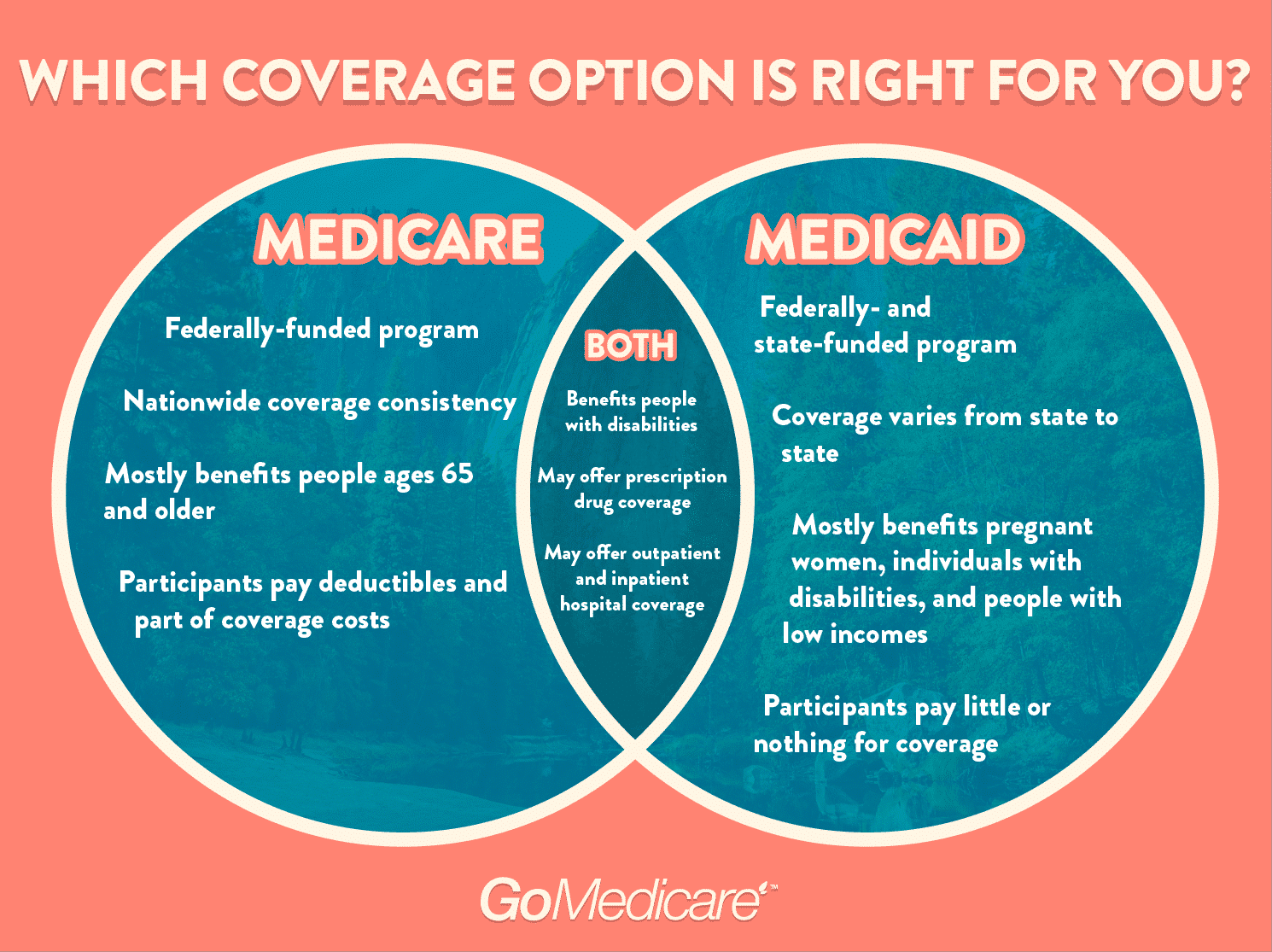
So, what’s the main difference between Medicare and Medicaid? In a nutshell, Medicare is a federal health insurance program designed specifically for seniors, individuals with disabilities, and those with certain chronic conditions, regardless of their income level. On the other hand, Medicaid is a joint federal-state program that provides health coverage to low-income individuals and families.
Let’s dive deeper into the specifics of each program.
Medicare: A Program for Seniors and Individuals with Disabilities
Medicare is a four-part program that provides health insurance coverage to approximately 63 million Americans. It’s designed for:
- Seniors aged 65 and older
- Individuals with disabilities under the age of 65
- Those with End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) or Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
The four parts of Medicare include:
- Part A (Hospital Insurance): Covers hospital stays, hospice care, and skilled nursing facility care
- Part B (Medical Insurance): Covers doctor visits, outpatient care, and medical equipment
- Part C (Medicare Advantage): A type of Medicare plan offered by private insurance companies that combines Part A and Part B benefits
- Part D (Prescription Drug Coverage): Offers prescription drug coverage to help manage medication costs
Medicaid: A Program for Low-Income Individuals and Families
Medicaid, also known as the Medical Assistance Program, is a joint federal-state program that provides health coverage to low-income individuals and families. Eligibility requirements for Medicaid vary from state to state, but generally, it’s designed for:
- Low-income individuals and families
- Pregnant women
- Children under the age of 19
- Individuals with disabilities
- Seniors who require long-term care
Medicaid coverage includes a wide range of benefits, such as:
- Doctor visits and hospital stays
- Prescription medications




