Making Sense of Your Medical Finances: Decoding Health Plans and Health Savings Accounts
When it comes to navigating the complex world of healthcare, understanding your financial options is crucial. Two popular choices that often get blended together are health plans and health savings accounts. While they work together to help you manage medical expenses, they serve distinct purposes and offer different benefits.
Let’s break down the key differences between these two often-confused concepts, empowering you to make informed decisions about your health and wealth.
What are Health Plans?
A health plan is essentially an insurance policy that covers a portion of your medical expenses. You pay a premium each month, and in return, your insurer reimburses you for some or all of the costs incurred during a doctor’s visit, hospital stay, or other medical services. Think of it as a safety net that protects you from unexpected medical bills.
Health plans vary widely in terms of coverage, deductibles, copays, and maximum out-of-pocket expenses. Some popular types of health plans include:
- HMOs (Health Maintenance Organizations): These plans have a network of participating doctors and hospitals, and you’ll often need a referral to see a specialist.
- PPOs (Preferred Provider Organizations): PPOs also have a network, but you can see any doctor you choose, albeit with varying degrees of coverage.
- HDHPs (High-Deductible Health Plans): These plans come with lower premiums, but higher deductibles and out-of-pocket expenses.
Now, enter the world of Health Savings Accounts.
What are Health Savings Accounts?
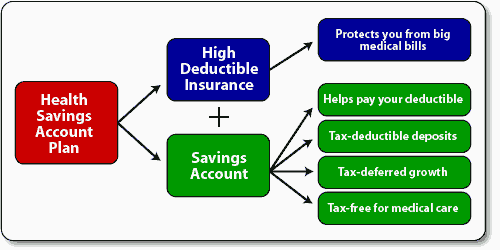
A Health Savings Account (HSA) is a tax-advantaged savings account designed to help you pay for medical expenses not covered by your health plan. To be eligible for an HSA, you must have a High-Deductible Health Plan (HDHP). Contributions to an HSA are tax-deductible, the funds grow tax-free, and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free as well.
Think of an HSA as a dedicated savings account for your out-of-pocket medical expenses, such as copays, prescriptions, and deductibles. You can contribute a certain amount each year, and the funds roll over if not used.
Key Differences Between Health Plans and HSAs
- Purpose: A health plan provides insurance coverage for medical expenses, while an HSA is a savings account to help cover out-of-pocket expenses.
- Eligibility: Anyone can purchase a health plan, but only those with High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs) are eligible for an HSA.
- Contributions: You pay premiums for a health plan, while you contribute funds to an HSA, which can be tax-deductible.
- Tax Benefits: Health plans don’t offer tax benefits, whereas HSAs provide tax-deductible contributions, tax-free growth, and tax-free withdrawals for qualified medical expenses.
- Portability: Health plans often have network restrictions, whereas HSAs are portable and owned by you, so you can take them with you if you change jobs or move.
To illustrate the relationship between health plans and HSAs, consider this example:
Let’s say you have an HDHP with a $2,000 deductible and a 20% copayment for doctor visits. You also have an HSA, to which you contribute $1,000 each year. When you need to see a doctor, you pay the copayment, and then use your HSA funds to cover the deductible. This way, you’ve minimized your out-of-pocket expenses and optimized your medical savings.
In conclusion, while health plans provide essential insurance coverage, Health Savings Accounts offer a tax-advantaged way to save for out-of-pocket medical expenses. By understanding the differences between these two financial tools, you can make informed decisions about your health and wealth, ensuring a more secure and prosperous future.




